-
Why Your Gum Line Recedes
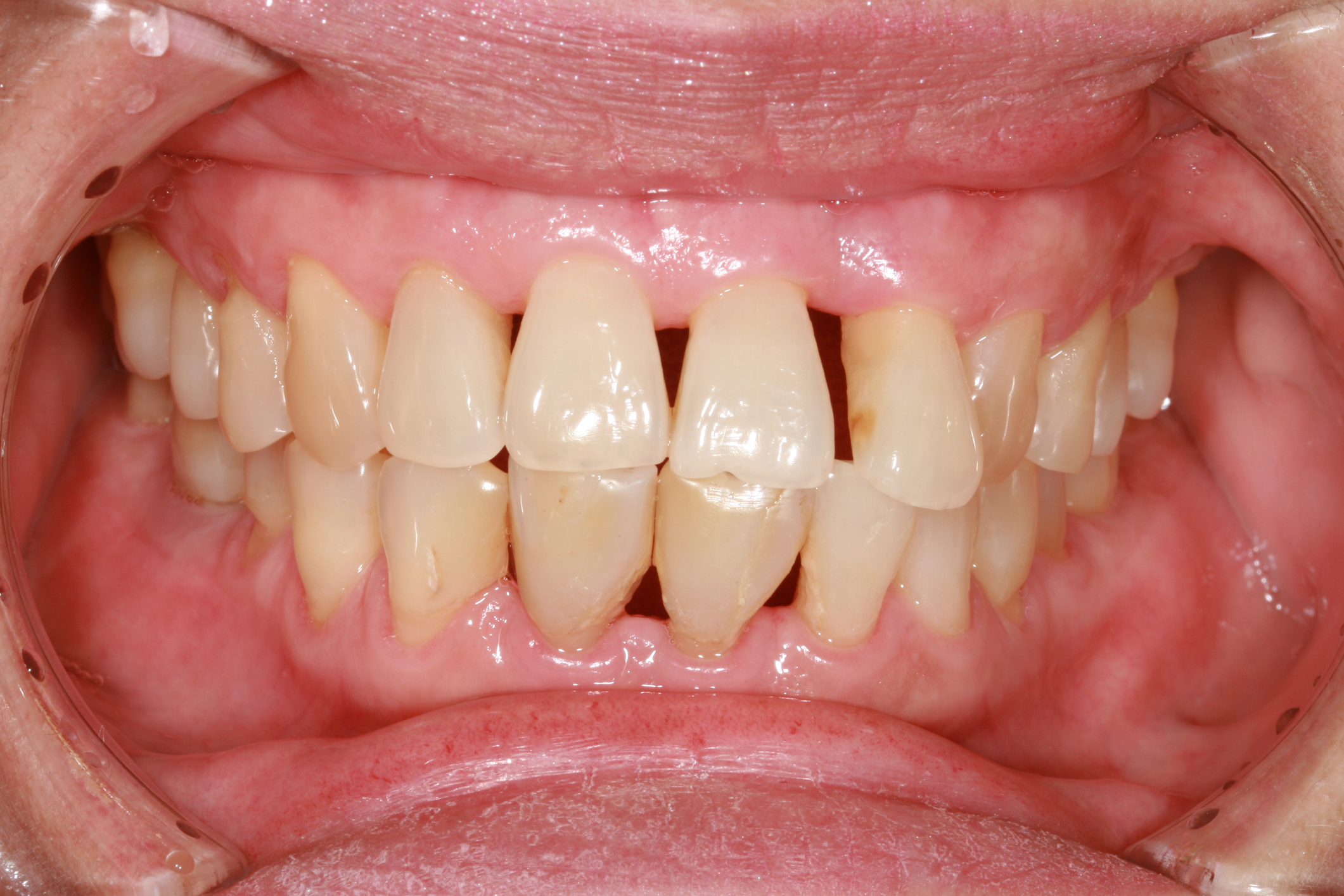
Gum recession.
How is your gum health? About half of all people over 30 suffer from periodontal disease, and this is the leading cause of gum recession. Gum recession is a problem, because when your gums recede too far, they can allow your teeth to fall out! Further, receding gums create pockets between the teeth and gums, and this can allow bacteria to grow and cause infections. In this way, even if your gum recession is not caused by periodontal disease, it can create an ideal environment for periodontal disease to progress. Once gums have receded, they don’t grow back, but there are some strategies you can employ to slow the recession. First, you need to know what is causing your gum line to recede.
- As mentioned, periodontal disease is a major cause of receding gums. The bacterial gum infections of periodontal disease can destroy not only gum tissue, but also the bone that holds the teeth in place. Catching periodontal disease in the early stage, called gingivitis, when the gums are simply inflamed, can help forestall its progression.
- It could be your genes. Sometimes, genetics just don’t work in your favor when it comes to your gums. About 30 percent of people have receding gums, leading to periodontal disease, no matter how well they care for their teeth.
- You might not be taking good care of your teeth. Poor oral hygiene can lead to tartar build-up, and when this happens, it can cause your gums to recede.
- On the other hand, you might be brushing too enthusiastically. Aggressive brushing can wear away your enamel and damage your gum tissue.
- Your teeth may be crooked. Believe it or not, misaligned teeth can wear on your gums. Teeth that don’t come together properly put too much force on the gums, causing them to recede.
- It might be hormones. Hormonal fluctuations, like the ones experienced during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can cause your gums to recede.
- Mouth trauma can damage your gums. If you get punched in the mouth or fall on your face, your teeth can be knocked loose, and your gums can sustain damage that causes recession.
- Your orthodontia may be the issue. It makes sense that using constant force to reposition your teeth could cause your gums to become inflamed and recede.
- If you grind your teeth, your gums might recede. In fact, receding gums may be your first warning sign that you grind your teeth at night.
- Tobacco use can lead to receding gums. Smoking and chewing tobacco are bad for your oral health in such a variety of ways that if you use tobacco, you really need to stop.
You might notice your gums receding, or you might notice some other warning signs. Your teeth may become sensitive to heat, cold, and sweets, or they may be sensitive when you’re brushing, flossing, or getting dental cleanings. You may also experience pain or discomfort near the gum line. Without treatment, gum recession could cause your teeth to feel loose. Fortunately, while receding gums won’t grow back, your dentist can help you slow the recession, as well as offering non-surgical and surgical treatments to improve the condition.
When you’re looking for a dentist to help with your teeth and gums, trust the dentist voted best in New York. At Park 56 Dental Group, we offer pediatric, prosthodontics, endodontics, oral surgery, Invisalign®, emergency, and sedation dentistry, all at the highest level of treatment. We serve the Midtown, Central Park, Upper East Side, Park Avenue, and all surrounding Manhattan and New York areas, with a patient-centered practice that has hours to fit your schedule. Schedule your complimentary consultation today by contacting us online or calling us at (212) 826-2322.
-
Is Coffee Ruining Your Teeth?

Fresh cup of coffee.
If you’re like most Americans, the day doesn’t quite start until you’ve had your morning coffee. Coffee is a delicious beverage that boosts your energy and may even be good for your heart health, but it can be hard on your smile, leaving your chompers less than pearly white. Beyond the stains it leaves behind, is coffee actually harmful? Could your morning cup of joe be ruining your teeth?
The answer is not as straightforward as you might think. If you’re a coffee drinker, you already know that it is a substance that stains. It will stain your favorite shirt, the upholstery in your car, your best tablecloth, and, yes, your teeth. It stains because it contains plant-based compounds called tannins that leave behind discoloration. The acidity in coffee helps with this staining because acid softens tooth enamel, making it easier for stains to penetrate the teeth. Because the stains seep through the enamel, though, coffee stains are difficult to remove with tooth brushing.
What’s more, as you get older, your tooth enamel begins to change, becoming more vulnerable and susceptible to staining. So, if you have a five cup a day coffee habit, you’re likely to have some noticeable stains after you’ve sustained it for several years. But beyond the yellowing teeth, does coffee do any damage?
There is, of course, the matter of coffee breath. Along with the acids, coffee introduces bacteria into your mouth, and it sticks to your tongue, causing halitosis. Fortunately, this is easily remedied by brushing your teeth after you drink coffee. Then, too, coffee is not alone in bringing bacteria into the environment of your mouth: any drink that isn’t water will do that. Fortunately, your saliva helps counteract the bacteria and allow your enamel to repair itself, but it’s important to brush and floss regularly to prevent cavities. Be aware that the sugar (or syrup) that goes into your coffee is much more damaging to your teeth than the coffee itself.
How can you continue to enjoy your coffee without staining your smile? You can’t, completely, but there are some things you can do to minimize the issue.
- Limit your coffee. Don’t drink coffee all day long, instead sticking to one or two cups of coffee at one time of day.
- Brush your teeth. Brushing with fluoride toothpaste after every cup is best because brushing removes bacteria and fluoride strengthens enamel. Bonus: you’ll lose the coffee breath. It is important to note, however, that you should wait about 30 minutes after your coffee to brush and floss, because immediately after you drink it your enamel will be soft enough to sustain damage from your toothbrush.
- Drink your coffee through a straw. When you use a straw, you can keep most of the coffee away from your teeth, which limits staining.
- Wash your coffee down with water. Water is always a good choice, whether you’re drinking coffee, eating food, or drinking alcoholic beverages. Why? Because water helps to keep the saliva flowing and rinses debris and bacteria away from your mouth.
- See your dentist regularly. Semi-annual cleanings can make a world of difference in the look of your teeth. Beyond just cleaning the teeth, they polish the enamel so that it can do a better job protecting your teeth from stains. Your dentist can also offer teeth whitening treatments to remove discoloration that has already appeared on your teeth.
If you are looking for a dentist to do those semi-annual cleanings and handle all your other dental needs, choose the dentist voted best in New York. At Park 56 Dental Group, we offer pediatric, prosthodontics, endodontics, oral surgery, Invisalign®, emergency, and sedation dentistry, all at the highest level of treatment. We serve the Midtown, Central Park, Upper East Side, Park Avenue, and all surrounding Manhattan and New York areas, with a patient-centered practice that has hours to fit your schedule. Schedule your complimentary consultation today by contacting us online or calling us at (212) 826-2322.
-
Reasons Why your Teeth are Temperature Sensitive
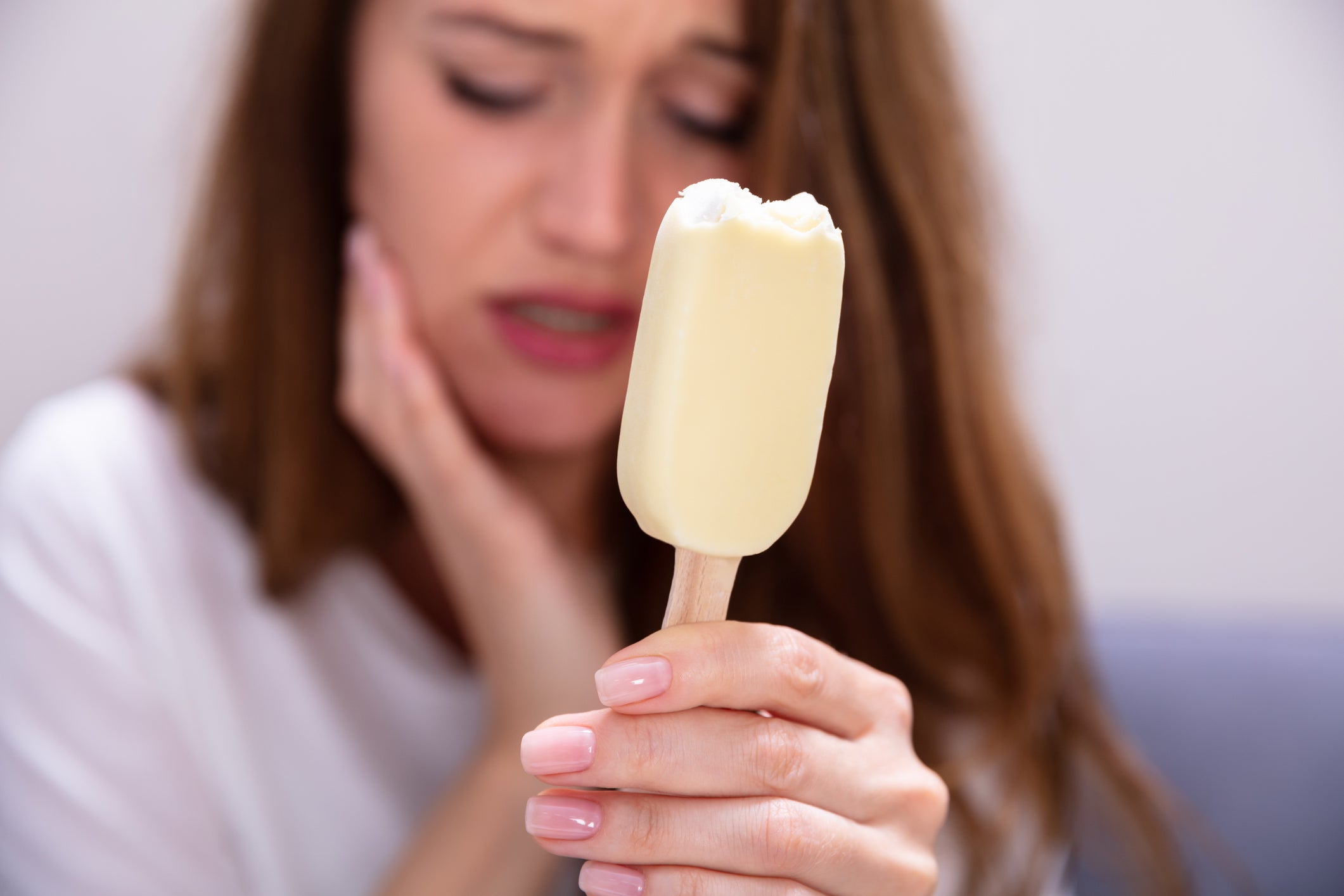

Do you find that eating ice cream or drinking hot coffee causes pain in your teeth? You may have sensitive teeth. It’s a common condition, affecting about 45 million people in the United States, but it can be painful and difficult. What causes teeth to be temperature sensitive? More importantly, what can be done about it?
Your dentist can help you determine the underlying cause of the sensitivity, though the reason teeth become sensitive is typically always the same. Teeth are made of three layers, the enamel, the dentin, and the pulp. The enamel is the hard, outer layer of the teeth, and it protects the softer, inner layers. Below the enamel is the dentin, which is made up of microscopic tubes leading to the innermost layer- the pulp. Within that pulp is the nerve system of the teeth, and dental sensitivity happens when the dentin layers or the nerves are stimulated by something hot or cold. The cause of this stimulation varies.
Cold sensitivity can be caused by tooth decay or gum disease. It can also be the result of brushing too aggressively, using abrasive toothpaste, or using a hard-bristled toothbrush, which can all wear away at the enamel. Tooth grinding or clenching can chip the teeth or damage tooth enamel, which can also cause sensitivity to cold. Receding gums and cracks in a tooth can leave that tooth vulnerable to the cold. If your teeth are sensitive to heat, though, it could have a different cause. Dental treatments like teeth whitening can lead to heat sensitivity, and so can teeth cleanings, root planning, and dental crown or filling placement. If you consume a diet that’s high in acids, found in foods like coffee, tomato sauce, and wine, it can lead to enamel loss and heat sensitivity. People struggling with gum disease often have sensitive teeth, because 80 percent of tooth sensitivity begins at the gum line.
If your teeth are highly sensitive and react to both heat and cold, the best thing to do is see a dentist to determine the cause and the best course of treatment. If the sensitivity is minor, though, you may be able to manage it at home. You can reduce the discomfort of mild temperature sensitivity by making a few changes.
- Instead of letting hot and cold liquids touch your teeth, use a straw.
- Reduce your consumption of acidic foods.
- Change to a softer bristled brush and be careful not to brush too hard.
- Switch to a toothpaste for sensitive teeth.
- Ask your dentist which mouthwash to use; some mouthwashes can irritate your dentin and pulp layers.
- Wear a mouthguard to prevent teeth grinding at night.
There are also treatments that dentists offer to improve dental sensitivity. If you find that your sensitivity is not improving after a few days, talk to your dentist about the best treatment for you. It could be as simple as fluoride therapy, or it could be a more involved procedure like a root canal or a gum graft. Dental restorations like a filling, inlay, onlay or crown can also protect damaged teeth and help with sensitivity. Nervous about seeing the dentist? We provide sedation dentistry for your comfort.
If you are looking for a dentist to help with tooth sensitivity, it makes sense to choose the practice voted Best in New York. At Park 56 Dental Group, we offer pediatric, prosthodontics, endodontics, oral surgery, Invisalign®, emergency, and sedation dentistry, all at the highest level of treatment. We serve the Midtown, Central Park, Upper East Side, Park Avenue, and all surrounding Manhattan and New York areas, with a patient-centered practice that has hours to fit your schedule. Schedule your complimentary consultation today by contacting us online or calling us at (212) 826-2322.
-
Foods to Eat When You Have a Toothache
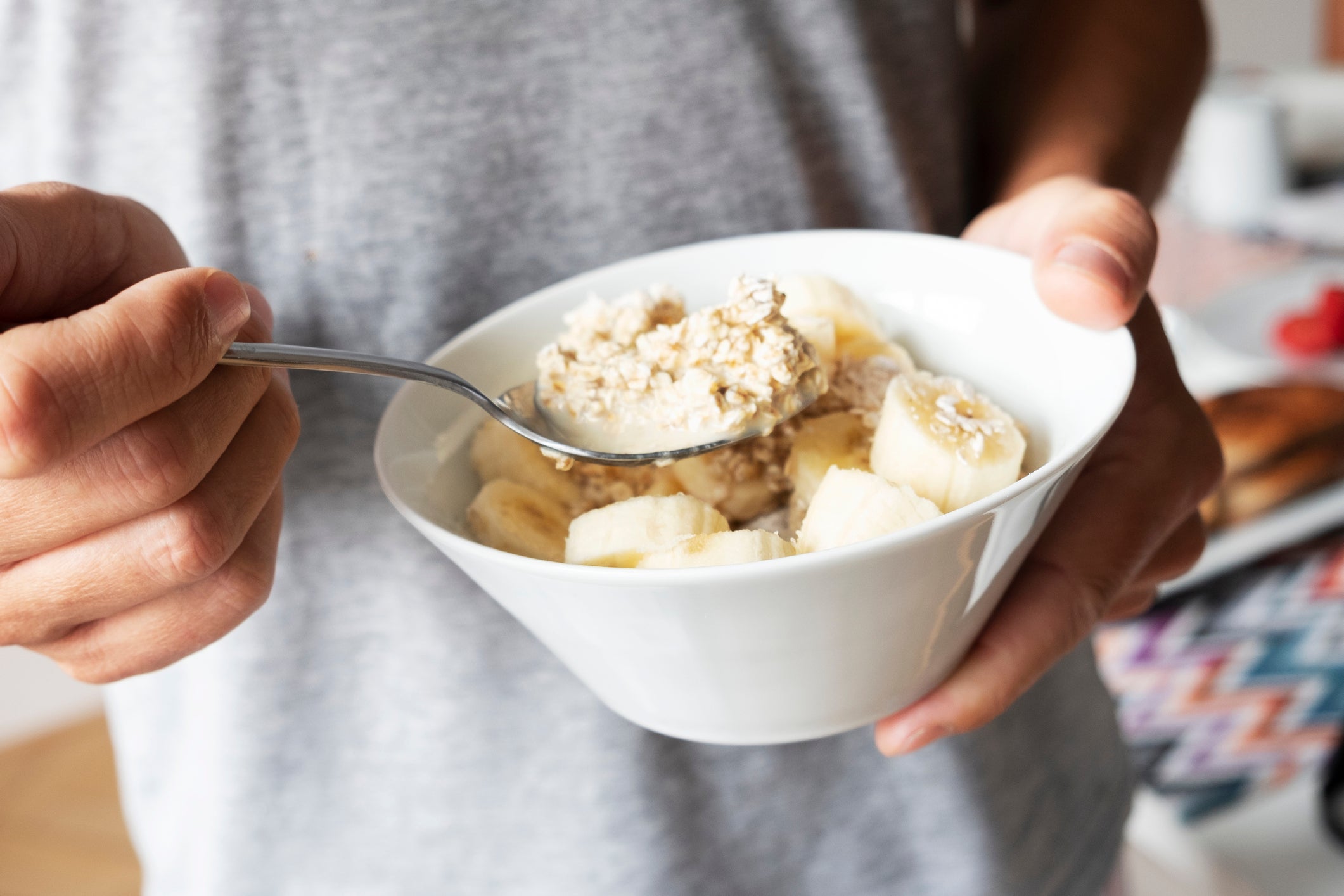

When you’ve got a toothache, one of the last things you want to do is eat. A tooth that’s throbbing is bad enough, but when you add chewing to the mix, it can be excruciating. Does this mean you are doomed to a liquid diet until you can see the dentist? Not necessarily. Here, we offer some strategies for reducing tooth pain, as well as recommendations about what to eat and not eat when your teeth are hurting.
First, let’s talk about toothaches themselves. Toothaches can happen for many reasons, including cavities and oral infections, but they can also be caused by dental procedures. Tooth extraction and oral surgery can cause pain during the recovery period, and even a cleaning can make your teeth feel sensitive and sore. Toothaches occur because the inner layer of the tooth, called the pulp, is inflamed, and gum inflammation can also cause tooth pain, because the gums surround the teeth. A toothache can feel sharp, throbbing, and sensitive, and you may experience a headache, fever, and a bad taste in your mouth at the same time.
Going to a dentist is the best course of action when you have a toothache, because sometimes toothaches can lead to more serious health conditions. However, there are some home remedies you can try to alleviate the pain while you are waiting for an appointment. A saltwater rinse may bring relief, or you could try a cold compress. Garlic, cloves, and peppermint tea have all been shown to reduce tooth pain, so you might want to give one of these tactics a shot.
There are also foods you can eat that won’t exacerbate the problem. Soft, easy to eat foods like bananas, applesauce, cottage cheese, mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs, and oatmeal are all good options if you have a toothache. Gelatin, puddings, custards, smoothies, and milkshakes can also be soothing, though ice cream is typically too cold to eat with a toothache. As long as it isn’t too warm or too cold, any soft food is a good option.
You will want to steer clear of any foods that are acidic or loaded with sugar. Avoid citrus fruits, tomatoes, raw vegetables, and anything spicy or salty. Things that are hard and crunchy or difficult to chew, like granola or meat, should be avoided. Hot coffee will likely be too painful to drink, and hard or sticky candy will cause more pain. Chewing ice should be avoided, because it’s not just hard on the teeth but also too cold to tolerate with a toothache.
The best thing to do when you have a toothache, of course, is to make an appointment with a highly skilled, experienced dentist. At Park 56 Dental Group, we offer pediatric, prosthodontics, endodontics, oral surgery, Invisalign®, emergency, and sedation dentistry, all at the highest level of treatment. We serve the Midtown, Central Park, Upper East Side, Park Avenue, and all surrounding Manhattan and New York areas, with a patient-centered practice that has hours to fit your schedule. Schedule your complimentary consultation today by contacting us online or calling us at (212) 826-2322.
-
Can a toothache cause problems to the rest of your body?

We know that the health of your mouth has an impact on your overall health, but does pain in your mouth cause problems for your body? When you have a toothache, it can certainly feel like your whole body is involved! Your head may throb, your heart may race, and you may feel nauseous or just generally sick. Is it all in your imagination?
In a word, no. A common cause of a toothache is tooth infection, and a tooth infection can definitely affect your whole body. Tooth infections happen when bacteria enter the tooth because of a chip or a cavity, and infections can lead to an abscess at the root of the tooth. An abscess causes constant, throbbing pain that can radiate to the jawbone, neck, or ear, along with bad breath, a bad taste in the mouth, and increased sensitivity to hot and cold foods.
Left untreated, the bacteria that caused your tooth infection can begin to spread throughout your body. If it spreads to the blood, it can cause sepsis, with symptoms that include an extremely high fever, respiratory trouble, and mental confusion. Your blood pressure may drop, causing you to go into septic shock, and in the worst case scenario, you could die. Another life-threatening condition that can result from a tooth infection is meningitis, which occurs because of inflammation near the brain and spinal cord. Ludwig’s Angina can also be caused by a tooth infection, bringing symptoms of pain and tenderness under the tongue, trouble swallowing, breathing, and speaking, swelling and redness of the neck, neck and ear pain, drooling, fever, chills, fatigue, confusion, and weakness. To avoid any of these complications and illnesses, it’s important to seek prompt medical treatment for a tooth infection. To prevent tooth infections, practice good oral hygiene, eat a nutrient-dense diet, and see your dentist regularly.
You don’t necessarily have to have a tooth infection to have your tooth pain affect other parts of your body. Because of a shared nerve, tooth pain can cause head pain. If you grind your teeth, it can cause muscle stress that results in both a toothache and a headache, and these can also both be caused by a sinus infection or TMJ (temporomandibular joint dysfunction). If your tooth hurts due to a cavity, crack, or impaction, you may get a migraine. It is thought that the connection between tooth pain and migraines has to do with a cranial nerve called the trigeminal nerve, which provides feeling to the face, including the mouth. Pain from a toothache can irritate this nerve and trigger a migraine.
If you have a toothache, don’t put off seeing an experienced dentist, who can determine the source of your pain and prevent it from affecting the rest of your body. At Park 56 Dental Group, we offer pediatric, prosthodontics, endodontics, oral surgery, Invisalign®, emergency, and sedation dentistry, all at the highest level of treatment. We serve the Midtown, Central Park, Upper East Side, Park Avenue, and all surrounding Manhattan and New York areas, with a patient-centered practice that has hours to fit your schedule. Schedule your complimentary consultation today by contacting us online or calling us at (212) 826-2322.
-
The Connection Between Asthma and Oral Health

Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people around the world. It is a condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing. It is well known that asthma triggers can come from a variety of sources, such as pollen, pollution, and other environmental factors. However, did you know that oral health can also play a significant role in asthma management? In this blog post, we will explore the connection between asthma and oral health.
Asthma and Gum Disease
Studies show that people with asthma are more likely to develop gum disease than those without asthma. Gum disease is an infection that affects the tissues and bones that support the teeth, and it can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. This is because the inflammation in the airways caused by asthma can also affect the gums. Furthermore, some of the medications used to treat asthma can have side effects that increase the risk of gum disease.
Asthma and Dry Mouth
Breathing through the mouth is a common symptom of asthma, especially during an attack. However, this can lead to dry mouth, which is a condition that reduces the amount of saliva in the mouth. Saliva is essential for a healthy mouth because it helps to wash away food particles and neutralize the acids that cause tooth decay. When there is not enough saliva, the risk of tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health issues increases.
Asthma and Oral Thrush
Oral thrush is a fungal infection that can affect the mouth and throat. People with asthma are at a higher risk of developing oral thrush because the medications used to treat asthma can weaken the immune system. Furthermore, the inhalers used to deliver medication can leave residue in the mouth, providing a breeding ground for yeast and bacteria.
Asthma and Teeth Grinding
Teeth grinding, or bruxism, is a condition that causes the grinding, clenching, or gnashing of teeth. People with asthma may be more likely to grind their teeth because asthma attacks can cause tension and stress, which can translate into clenching and grinding during sleep. Teeth grinding can lead to a host of oral health issues, such as tooth sensitivity, cracked teeth, and jaw pain.
Asthma and Oral Care
Proper oral care is essential for people with asthma because it can help to prevent oral health issues and reduce the risk of respiratory infections. This includes brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash. Additionally, people with asthma should rinse their mouth with water after using their inhaler to reduce the risk of dry mouth and oral thrush.
Contact Park 56 Dental in New York Today for More Tips!
Asthma and oral health are closely linked. People with asthma are at a higher risk of developing gum disease, dry mouth, oral thrush, and teeth grinding. However, by practicing proper oral hygiene and working closely with your dentist, you can reduce the risk of these issues and improve your overall health. At Park 56 Dental, we are dedicated to helping our patients maintain healthy mouths and bodies. If you have asthma or any other respiratory condition, please let us know so that we can provide you with the best possible care.
-
The Connection Between Your Dental Health and Vision

You care for your teeth to keep them healthy and strong, but, as you may know, poor dental health can negatively affect other systems in your body. There is a connection between diabetes and gum disease, for instance, and bacteria from tooth decay can impact your heart health. What you may not realize, though, is that there is a connection between your dental health and your vision. Could caring for your teeth actually protect your vision?
What is the connection between oral health and eye health? According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, oral infections, including periodontal disease, cause an inflammatory response that can damage the optic nerve and cause vision loss. Additionally, people who have old mercury fillings may be at risk for vision problems that include iritis, color-vision issues, retinitis pigmentosa, and the formation of cataracts.
Poor dental hygiene is also known to contribute to the development of open-angle glaucoma. A degenerative eye disease, open-angle glaucoma results from increased fluid build-up in the eye that places damaging pressure on the optic nerve. Left untreated, this condition can cause vision loss and even blindness. One recent study found that the number of natural teeth a person has, an indication of the person’s dental care, is related to the risk of developing glaucoma.
While seeing an eye doctor is important for keeping your eyes healthy, it seems to be just as important to practice good dental habits. These habits include brushing teeth at least twice a day and flossing at least once, rinsing daily with an anti-bacterial mouthwash, having old fillings replaced with safer materials, and seeing a dentist for gingivitis treatment or a root canal for a badly diseased tooth. Eating a nutrient-dense diet and avoiding unhealthy practices like smoking and using your teeth for things unrelated to chewing food are also healthy habits. It is also a good practice to see a dentist twice a year for preventative cleanings and follow-up exams.
One of the most important factors when it comes to caring for your teeth is finding a good dentist. At Park 56 Dental Group, we offer pediatric, prosthodontics, endodontics, oral surgery, Invisalign®, emergency, and sedation dentistry, all at the highest level of treatment. We serve the Midtown, Central Park, Upper East Side, Park Avenue, and all surrounding Manhattan and New York areas, with a patient-centered practice that has hours to fit your schedule. Schedule your complimentary consultation today by contacting us online or calling us at (212) 826-2322.
-
Does menopause affect your oral health?

Menopause is a time of life that brings many unpleasant surprises. Hot flashes, insomnia, and mood swings are some of the commonly known symptoms that affect women going through this stage. Less known is the impact of fluctuating hormone levels on the mouth, but there definitely seems to be a link. As estrogen levels decrease during perimenopause and menopause, many women notice sensitive teeth, painful gums, dry mouth, and other issues.
- Hormonal fluctuations can cause tooth sensitivity. If you often find that your teeth hurt after you eat or drink hot or cold things, you may have sensitive teeth. This condition happens when the inner part of the teeth, the dentin, lose their enamel and cementum coatings, leaving the nerves inside vulnerable.
- Gum inflammation is another side effect of menopause. Women going through menopause might experience gingivostomatitis, an oral health condition that causes gum inflammation and canker sores. Periodontal disease can also develop due to low estrogen levels, leading to gum inflammation, bright red or purple gums, gum tenderness and bleeding, receding gums, pus formation, bad breath, bite issues, and loose teeth or gaps between the teeth. Interestingly, another problem that often occurs with menopause is lowered bone density, which can cause bone loss in the jawbone. The treatment for this condition often includes bisphosphonate drugs, which also help prevent the progression, of periodontal disease. Your dentist or periodontist can also treat periodontal disease by scaling to remove tarter, prescribing antimicrobial oral rinses or oral antibiotics, or performing flap surgery. For severe disease, bone or tissue grafts may be necessary. Practicing impeccable oral hygiene is a major part of controlling periodontal disease, and so is quitting smoking.
- Changes in hormone levels can change the way food tastes. Salty, sour, or peppery foods bother some women, and food can sometimes taste unusually bitter or metallic. Sometimes, these menopause-related taste changes are accompanied by a condition known as burning mouth. As the name implies, burning mouth causes burning, pain, and tenderness around the mouth, including the lips tongue, and cheeks.
- Tooth pain can be caused by menopausal changes. For example, declining estrogen levels can decrease the thickness of the oral mucosal epithelium, leading to greater sensitivity to pain and higher vulnerability to mouth infections.
- Dropping hormones can cause dry mouth. Hormones help support saliva production and maintain the consistency of the saliva, but lower levels of estrogen can decrease your mouth’s ability to produce saliva. Dry mouth makes it uncomfortable to eat, but it can also cause gum sensitivity, mouth ulcers, sore gums, an increase in infections, and cavities.
Often, doctors prescribe hormone replacement therapy to help combat the signs of menopause. However, it’s also important to work with your dentist to keep your oral health in good shape. Regular cleanings and check-ups, brushing and flossing daily, taking supplements like calcium and vitamin D, and using products to treat sensitive teeth and dry mouth can all be part of maintaining oral health during menopause. It’s also important to have a good dentist.
At Park 56 Dental Group, we offer pediatric, prosthodontics, endodontics, oral surgery, Invisalign®, emergency, and sedation dentistry, all at the highest level of treatment. We serve the Midtown, Central Park, Upper East Side, Park Avenue, and all surrounding Manhattan and New York areas, with a patient-centered practice that has hours to fit your schedule. Schedule your complimentary consultation today by contacting us online or calling us at (212) 826-2322.
-
How Staying Hydrated Can Help Improve Your Dental Health

You hear it from everyone: drink more water. Experts advise drinking about eight glasses of water each day to help improve your health. Water is good for you for many reasons; it helps you detox, keeps your skin plump, youthful, and clear, and may even reduce your risk of certain cancers. It helps just about every system in the body, from your circulation to your muscles, and it’s no wonder, because we’re made of about 60 percent water. What you may not know, though, is that in addition to all those benefits, remaining well hydrated can improve your dental health. Let’s take a closer look at why that’s true.
- Water strengthens teeth. Water, especially fluoridated water, contains fluoride and other minerals that help restore the calcium and phosphorous levels in dental enamel. Did you know that in communities with fluoridated water, each dollar spent on fluoridation saves about $38 in dental healthcare costs? Drinking water is especially important for young children because it strengthens teeth as they are forming, making them more cavity-resistant throughout the child’s life.
- Drinking water helps clean the mouth. Drinking sugary beverages like soda, sports drinks, and juice can cause sugars to remain on the surface of the teeth. This leads to growth of the bacteria in plaque, which release harmful acids that degrade tooth enamel and cause decay. Drinking water, on the other hand, washes away food residue and discourages bacterial growth. Because food residue and bacteria cause bad breath, people who drink a lot of water have better smelling breath. Drinking water isn’t a substitute for brushing and flossing, but it can be an important part of your dental care routine.
- Dry mouth can be alleviated by drinking water. This makes sense, because saliva is 99 percent water. Dry mouth is a condition in which the mouth does not produce enough saliva, making it harder to chew and swallow, and causing an elevated risk of tooth decay. Drinking water hydrates the mouth and stimulates saliva production, making it a powerful weapon against dry mouth.
- Water can help prevent stains on the teeth. Foods and beverages like coffee, tomato sauce, wine, curry, and citrus fruits can leave behind stains, but drinking water in between bites or sips can quickly rinse away residue before it has the chance to settle into a stain.
- Water is a calorie free beverage. Consumption of sugary beverages contributes to the rising obesity rate in the United States, and people who drink more than one sugary beverage per day are nearly 30 percent more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. Water has no calories and no sugar, making it a much healthier option.
At Park 56 Dental Group, we offer pediatric, prosthodontics, endodontics, oral surgery, Invisalign®, emergency, and sedation dentistry, all at the highest level of treatment. We serve the Midtown, Central Park, Upper East Side, Park Avenue, and all surrounding Manhattan and New York areas, with a patient-centered practice that has hours to fit your schedule. Schedule your complimentary consultation today by contacting us online or calling us at (212) 826-2322.
-
Do Genetics Play a Role in Your Dental Health?

At Park 56 Dental, we understand that genetics play a role in your overall health, but did you know that it also plays a role in your dental health? While good oral hygiene habits can go a long way towards protecting your teeth and gums, genetics determine how predisposed you are to certain dental issues. Let’s break down the role of genetics in dental health.
Dental Caries
One of the most common dental problems is tooth decay or cavities. Cavities can be caused by poor oral hygiene habits, but they can also be a result of genetic factors. Studies have found that some people may develop more cavities than others due to their genetic makeup. For example, if you have a family history of cavities, then you may be more likely to develop them yourself.
Tooth Wear and Tear
In addition to cavities, tooth wear and tear can also be affected by genetics. Some people may be genetically predisposed to having weaker teeth than others which make them more prone to experiencing wear and tear earlier in life. This is especially true for those with thinner enamel which makes it harder for their teeth to withstand the pressures of daily activities like chewing and grinding.
Misaligned Teeth
One of the most common effects of genetics on oral health is misaligned (crooked) teeth. In many cases, crooked teeth are caused by genetic factors such as jaw size and shape, or even a difference in the length of two sides of the jaw. If you have crooked teeth, Park 56 Dental in New York can help with orthodontic treatments like braces and Invisalign® to help straighten them out.
Teeth Color
The color of your teeth is another trait that can be influenced by genetics. Some people have naturally whiter teeth than others due to inherited traits, while others may have naturally yellowish or grayish tints to their smile due to genetics as well. Park 56 Dental offers professional whitening services that can help brighten up any shade of smile.
Periodontal Disease
Genetics can also play a role in periodontal (gum) disease as well as other diseases such as diabetes and cancer that may affect your oral health. If you have any family members who have experienced gum disease or other serious dental problems, then you may be at an increased risk for developing these issues as well. It is important to keep track of any family history related to your dental health so that you can take steps to prevent any potential problems from occurring.
Reach Out to Park 56 Dental to Protect Your Smile!
The bottom line is that genetics do play a role in your dental health, but good oral hygiene habits are still important for keeping your teeth and gums healthy. So, if you want to protect yourself from potential dental problems down the road, make sure you brush twice daily, floss once daily, rinse with an antiseptic mouthwash regularly and visit Park 56 Dental at least twice a year for check-ups and cleanings! By taking these steps now, you’ll ensure that your smile remains healthy for many years to come!
RECENT POSTS
categories
- Uncategorized
- Cosmetic Dentistry
- Veneers
- Healthier Teeth
- Teeth Whitening
- Dental Health
- Video
- Dental Emergencies
- Invisalign
- Dental Implants
- Root Canal
- Sedation Dentistry
- Infographic
- Dental Crowns and Bridges
- Dental Anxiety
- Gum Disease
- COVID-19
- Bad Breath
- New York Dentist
- Cut out sugar
- General Dentistry
- Oral Health
- Oral Cancer
- Dry Mouth
- Gum Health
- Toothache
